Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a
-ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a  -ray field
-ray fieldKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Terasaka, Yuta; Tomita, Hideki*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Uritani, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167636_1 - 167636_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:90.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)We focus on the thickness and property controls of inorganic scintillators used for thermal neutron detection in intense  -ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20
-ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20 (a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF
(a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF :Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a
:Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron detection for GS20
-ray field, the neutron detection for GS20 with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a
with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron/
-ray field, the neutron/ -ray discrimination of GS20
-ray discrimination of GS20 was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
 -rays of fuel debris
-rays of fuel debrisMatsumura, Taichi; Okumura, Keisuke; Fujita, Manabu*; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 199, p.110298_1 - 110298_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Chemistry, Physical) Co radiation source under an intense
Co radiation source under an intense  Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr
Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields
spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.983 - 992, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology) -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 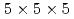
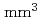 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0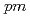 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:89.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
 Cf for safeguards verification measurements
Cf for safeguards verification measurementsRodriguez, D.; Rossi, F.; Takahashi, Tone; Seya, Michio; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 148, p.114 - 125, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Hagiwara, Kaito*; Yano, Takatomi*; Das, P. K.*; Lorenz, S.*; Ou, Iwa*; Sakuda, Makoto*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.023D01_1 - 023D01_26, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:87.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationSano, Yuichi; Ambai, Hiromu; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Iijima, Shizuka; Uchida, Naoki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 493, p.200 - 206, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:56.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, we investigated the effect of chloride ion on the corrosion behavior of SUS316L stainless steel, which is a typical material for the equipment used in reprocessing, in HNO solution containing seawater components, including under the
solution containing seawater components, including under the  -ray irradiation condition. Electrochemical and immersion tests were carried out using a mixture of HNO
-ray irradiation condition. Electrochemical and immersion tests were carried out using a mixture of HNO and artificial seawater (ASW). In the HNO
and artificial seawater (ASW). In the HNO solution containing high amounts of ASW, the cathodic current densities increased and uniform corrosion progressed. This might be caused by strong oxidants, such as Cl
solution containing high amounts of ASW, the cathodic current densities increased and uniform corrosion progressed. This might be caused by strong oxidants, such as Cl and NOCl, generated in the reaction between HNO
and NOCl, generated in the reaction between HNO and Cl
and Cl ions. The corrosion rate decreased with the immersion time at low concentrations of HNO
ions. The corrosion rate decreased with the immersion time at low concentrations of HNO , while it increased at high concentrations. Under the
, while it increased at high concentrations. Under the  -ray irradiation condition, the corrosion rate decreased due to the suppression of the cathodic reactions by the reaction between the above oxidants and HNO
-ray irradiation condition, the corrosion rate decreased due to the suppression of the cathodic reactions by the reaction between the above oxidants and HNO generated by radiolysis.
generated by radiolysis.
 -ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt
-ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea saltMotooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
In Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), seawater was injected into spent fuel pools in March 2011. Zircaloy-2 is adopted for the fuel cladding at 1F. Zirconium alloys including Zircaloy-2 are susceptible to pitting corrosion in oxidizing chloride solutions. In this study, we investigated the effect of oxide film formed during  -ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt. The pitting potentials of Zircaloy-2 were measured using the water containing artificial sea salt. Changes in the composition of water containing sea salt were analyzed before and after
-ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt. The pitting potentials of Zircaloy-2 were measured using the water containing artificial sea salt. Changes in the composition of water containing sea salt were analyzed before and after  -ray irradiation. The characteristics of the oxide films formed on Zircaloy-2 were evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Solution analyses for water containing sea salt showed that hydrogen peroxide was generated by the irradiation. The pitting potential of Ziracloy-2 with oxide film formed under
-ray irradiation. The characteristics of the oxide films formed on Zircaloy-2 were evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Solution analyses for water containing sea salt showed that hydrogen peroxide was generated by the irradiation. The pitting potential of Ziracloy-2 with oxide film formed under  -ray irradiation was higher than that with oxide film formed without irradiation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that the oxide film was composed of zirconium oxide and the growth of oxide film was enhanced during the irradiation. It could thus be explained that the enhanced growth of oxide film under
-ray irradiation was higher than that with oxide film formed without irradiation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that the oxide film was composed of zirconium oxide and the growth of oxide film was enhanced during the irradiation. It could thus be explained that the enhanced growth of oxide film under  -ray irradiation caused the higher pitting potential.
-ray irradiation caused the higher pitting potential.
Sono, Hiroki; Ono, Akio*; Kojima, Takuji; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Yamane, Yoshihiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(3), p.276 - 284, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)For a study on the applicability of a personal dosimetry method to criticality accident dosimetry, an assessment of the human body surface and internal dose estimations was performed by experimental and computational simulations. The experimental simulation was carried out in a criticality accident situation at the TRACY facility. The neutron and  -ray absorbed doses in muscle tissue were separately estimated by a dosimeter set of an alanine dosimeter and a thermoluminescence dosimeter made of enriched lithium tetra borate with a phantom. The computational simulation was conducted with a Monte Carlo code taking account of dose components of neutrons, prompt
-ray absorbed doses in muscle tissue were separately estimated by a dosimeter set of an alanine dosimeter and a thermoluminescence dosimeter made of enriched lithium tetra borate with a phantom. The computational simulation was conducted with a Monte Carlo code taking account of dose components of neutrons, prompt  -rays and delayed
-rays and delayed  -rays. The computational simulation was ascertained to be valid by comparison between the calculated dose distributions in the phantom and the measured ones. The assessment based on the experimental and computational simulations confirmed that the personal dosimetry using the dosimeter set provided a first estimation of the body surface and internal doses with precision.
-rays. The computational simulation was ascertained to be valid by comparison between the calculated dose distributions in the phantom and the measured ones. The assessment based on the experimental and computational simulations confirmed that the personal dosimetry using the dosimeter set provided a first estimation of the body surface and internal doses with precision.
 (Ce) scintillation detector applications for environmental
(Ce) scintillation detector applications for environmental  -ray measurements of low to high dose rates
-ray measurements of low to high dose ratesTsutsumi, Masahiro; Tanimura, Yoshihiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 557(2), p.554 - 560, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:68.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new cerium-doped LaCl (Ce) scintillator is evaluated with respect to the application in environmental
(Ce) scintillator is evaluated with respect to the application in environmental  -ray dosimetry and spectrometry. The scintillator is very attractive for
-ray dosimetry and spectrometry. The scintillator is very attractive for  -ray spectrometry in the case of high count rate, because it has excellent energy resolution and fast decay time. The performance characteristics of a scintillator with a 25.4 mm
-ray spectrometry in the case of high count rate, because it has excellent energy resolution and fast decay time. The performance characteristics of a scintillator with a 25.4 mm  25.4 mm LaCl
25.4 mm LaCl (Ce) crystal are studied and compared to those of a NaI(Tl) scintillator with the same size crystal. Acquired pulse-height spectra are converted to dose rates by using the G(E) function method. Though the LaCl
(Ce) crystal are studied and compared to those of a NaI(Tl) scintillator with the same size crystal. Acquired pulse-height spectra are converted to dose rates by using the G(E) function method. Though the LaCl (Ce) crystal itself produces a rather high background in the crystal itself, the scintillator provides good energy information and dose-rate readings from low to high-level (several mGy/h) by subtracting the self-background. The properties of LaCl
(Ce) crystal itself produces a rather high background in the crystal itself, the scintillator provides good energy information and dose-rate readings from low to high-level (several mGy/h) by subtracting the self-background. The properties of LaCl (Ce) scintillator suggest that the scintillator could be a promising candidate for monitoring at high-dose levels as in emergencies, as well as at ordinary levels of background radiation.
(Ce) scintillator suggest that the scintillator could be a promising candidate for monitoring at high-dose levels as in emergencies, as well as at ordinary levels of background radiation.
Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.181 - 182, 2006/01
The yields of OH radicals in water containing phenol have been investigated for several ten MeV/n C ion and Ne ion having the same LET value, as a function of the residual ion energy at the specific depth in water. In this study, beside such energy dependence, the dependence of reaction time of OH radical yield was examined by changing the concentration of phenol as solute. The defferential G'-values of OH radicals, those G-values per kinetic energy of ions increase with specific energy of Ne ions. The G'-value just after irradiation(1.5ns) is relatively high but become lower with reaction time to be the value (2.7) obtained for  Co
Co  -rays. It suggests the diffusion behavior of OH radicals locally induced in water.
-rays. It suggests the diffusion behavior of OH radicals locally induced in water.
 -nonylphenols in water and elimination of their estrogen activities by
-nonylphenols in water and elimination of their estrogen activities by  Co
Co  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Otani, Yoshimi*; Takigami, Machiko; Shimada, Yoshitaka*; Kojima, Takuji; Hiratsuka, Hiroshi*; Namba, Hideki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 75(1), p.61 - 69, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.83(Chemistry, Physical)Decomposition of  -Nonylphenols (NPs) in water at 1
-Nonylphenols (NPs) in water at 1  mol dm
mol dm was decreased exponentially with absorbed dose when NPs were irradiated by
was decreased exponentially with absorbed dose when NPs were irradiated by  Co
Co -rays. Two products having molecular weight of 236, presumably OH adducts of NPs, were detected by LC-MS analyses. The elimination of estrogen activity of aqueous NPs solution including such irradiation products at 5000 Gy (J kg
-rays. Two products having molecular weight of 236, presumably OH adducts of NPs, were detected by LC-MS analyses. The elimination of estrogen activity of aqueous NPs solution including such irradiation products at 5000 Gy (J kg ) was confirmed by the yeast two hybrid assay. These results should expand the application of ionizing radiation to the treatment of NPs.
) was confirmed by the yeast two hybrid assay. These results should expand the application of ionizing radiation to the treatment of NPs.
Nishitani, Takeo; Sugie, Tatsuo; Morishita, Norio; Yokoo, Noriko*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 74(1-4), p.871 - 874, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 -ray spectrometry for the rapid radioactivity evaluation of solidified products prepared from radioactive wastes
-ray spectrometry for the rapid radioactivity evaluation of solidified products prepared from radioactive wastesHaraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Hoshi, Akiko; Yonezawa, Chushiro*; Nakashima, Mikio
JAERI-Tech 2005-050, 35 Pages, 2005/09
Non-destructive  -ray spectrometry has been examined as a simple and rapid radioactivity measurement technique for the solidified products prepared by plasma melting for low level radioactive miscellaneous wastes generated from nuclear facilities. The Compton background resulting from the coexisting radionuclides pose a problem in the usual
-ray spectrometry has been examined as a simple and rapid radioactivity measurement technique for the solidified products prepared by plasma melting for low level radioactive miscellaneous wastes generated from nuclear facilities. The Compton background resulting from the coexisting radionuclides pose a problem in the usual  -ray spectrometry which uses only a Ge detector. In order to reduce the background count and to measure the interested nuclide selectively, the coincidence and the anti-coincidence
-ray spectrometry which uses only a Ge detector. In order to reduce the background count and to measure the interested nuclide selectively, the coincidence and the anti-coincidence  -ray spectrometry using the Ge-BGO detector system were examined. As a result of applying the anti-coincidence
-ray spectrometry using the Ge-BGO detector system were examined. As a result of applying the anti-coincidence  -ray spectrometry to a single
-ray spectrometry to a single  -ray emitter
-ray emitter  Cs and the coincidence
Cs and the coincidence  -ray spectrometry to multiple
-ray spectrometry to multiple  -ray emitter
-ray emitter  Eu under existence of
Eu under existence of  Co, the detection limits of
Co, the detection limits of  Cs and
Cs and  Eu in the sample, which contained
Eu in the sample, which contained  Co, were reduced by a factor of about 6 and 1.5, respectively. It was confirmed that the present methods are useful for the
Co, were reduced by a factor of about 6 and 1.5, respectively. It was confirmed that the present methods are useful for the  -activity measurement of solidified products.
-activity measurement of solidified products.
 No and its
No and its  -decay daughter
-decay daughter 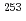 Fm
FmAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Akiyama, Kazuhiko; Osa, Akihiko; Oura, Yasuji*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 95(10), p.102502_1 - 102502_4, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:87.64(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excited states in  Fm fed by the
Fm fed by the  decay of
decay of  No have been established through
No have been established through  -
- and
and  -electron coincidence spectroscopy using a gas-jet transport system and an on-line isotope separator. The spin-parity of the 124.1 keV level in
-electron coincidence spectroscopy using a gas-jet transport system and an on-line isotope separator. The spin-parity of the 124.1 keV level in  Fm has been identified on the basis of the measured internal conversion coefficients. The
Fm has been identified on the basis of the measured internal conversion coefficients. The ![$$nu 3/2^{+}[622]$$](/search/images/EROG23JAGMXTEXT1FN4VWNRSGJOSI.gif) configuration has been assigned to the ground state of
configuration has been assigned to the ground state of  No as well as to the 124.1 keV level. It was found that the ground state configuration of
No as well as to the 124.1 keV level. It was found that the ground state configuration of  No is different from that of lighter
No is different from that of lighter 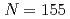 isotones.
isotones.
 -ray absorbed doses inside human body in criticality accident situations using phantom and tissue-equivalent dosimeters
-ray absorbed doses inside human body in criticality accident situations using phantom and tissue-equivalent dosimetersSono, Hiroki; Kojima, Takuji; Soramasu, Noboru*; Takahashi, Fumiaki
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.315 - 320, 2005/08
Personal dosimeters provide a fundamental evaluation of external exposures to human bodies in radiation accidents. The dose distribution inside the body, which is needed to estimate the exposures from a result of personal dosimetry, has been evaluated mostly by computational simulations, while experimental data to verify the simulations are not sufficiently supplied, in particular, in criticality accident situations. For the purpose of obtaining the experimental data on external exposures inside the body, a preliminary experiment on criticality accident dosimetry was carried out at the Transient Experiment Critical Facility (TRACY) using a human phantom and tissue-equivalent dosimeters. The neutron and  -ray absorbed doses inside the phantom could be satisfactorily measured by the combined use of an alanine dosimeter and a thermoluminescent dosimeter made of enriched lithium tetra borate. The doses measured in and on the phantom were regarded as reasonable in dose level and distribution by comparison with the doses measured in the free air.
-ray absorbed doses inside the phantom could be satisfactorily measured by the combined use of an alanine dosimeter and a thermoluminescent dosimeter made of enriched lithium tetra borate. The doses measured in and on the phantom were regarded as reasonable in dose level and distribution by comparison with the doses measured in the free air.
 -ray dose components in criticality accident situations
-ray dose components in criticality accident situationsSono, Hiroki; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi*; Ono, Akio*; Kojima, Takuji; Soramasu, Noboru*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(8), p.678 - 687, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)Component analysis of  -ray doses in criticality accident situations is indispensable for further understanding on emission behavior of
-ray doses in criticality accident situations is indispensable for further understanding on emission behavior of  -rays and accurate evaluation of external exposure to human bodies. Such dose components were evaluated, categorizing
-rays and accurate evaluation of external exposure to human bodies. Such dose components were evaluated, categorizing  -rays into four components: prompt, delayed, pseudo components in the period of criticality, and a residual component in the period after the termination of criticality. This evaluation was performed by the combination of dosimetry experiments at the TRACY facility using a thermoluminescent dosimeter (TLD) made of lithium tetra borate and computational analyses using a Monte Carlo code. The evaluation confirmed that the dose proportions of the above components varied with the distance from the TRACY core tank. This variation was due to the difference in attenuation of the individual components with the distance from the core tank. The evaluated dose proportions quantitatively clarified the contribution of the pseudo and the residual components to be excluded for accurate evaluation of
-rays into four components: prompt, delayed, pseudo components in the period of criticality, and a residual component in the period after the termination of criticality. This evaluation was performed by the combination of dosimetry experiments at the TRACY facility using a thermoluminescent dosimeter (TLD) made of lithium tetra borate and computational analyses using a Monte Carlo code. The evaluation confirmed that the dose proportions of the above components varied with the distance from the TRACY core tank. This variation was due to the difference in attenuation of the individual components with the distance from the core tank. The evaluated dose proportions quantitatively clarified the contribution of the pseudo and the residual components to be excluded for accurate evaluation of  -ray exposure.
-ray exposure.
Shibata, Yasushi*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Hori, Naohiko; Kishi, Toshiaki; Kumada, Hiroaki; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Nakai, Kei*; et al.
JAERI-Research 2005-009, 41 Pages, 2005/03
The measurement of neutron flux and boron concentration in the blood during medical irradiation is indispensable in order to evaluate the radiation in boron neutron capture therapy. It is, however, difficult to measure the blood boron concentration during neutron irradiation because access to the patient is limited. Therefore we prospectively investigated the predictability of blood boron concentrations using the data obtained at the first craniotomy after infusion of a low dosage of BSH. When the test could not be carried out, the blood boron concentration during irradiation was also predicted by using the 2-compartment model. If the final boron concentration after the end of the infusion is within 95% confidence interval of the prediction, direct prediction from biexponential fit will reduce the error of blood boron concentrations during irradiation to around 6%. If the final boron concentration at 6 or 9 hours after the end of infusion is out of 95% confidence interval of the prediction, proportional adjustment will reduce error and expected error after adjustment to around 12%.
Kawasaki, Katsuya
Hoken Butsuri, 40(1), p.56 - 60, 2005/03
The centralized radioactivity measurement system has been used to carry out intensively measurements of a large number and variety of samples that are necessary for the control of radioactivity in the facilities of the JAERI Tokai Establishment and its environment. The operation of the system started in 1981, and presently the system processes more than 20,000 samples a year. However, the computers of the system have aged so much that the manufacturer's support and stable operation are no longer sure. Therefore, we renewed and restructured the computer system in 2003. A client-server system was adopted in the new system. The information of samples can be registered through the intranet. The clients can also confirm the progress of processing of their samples and browse the analytical results from their own computers. The renewed system can provide some convenience functions to the clients. This report is introduced about the centralized radioactivity measurement system.